Çifci, G. & Çelebi, S. S. & Parlaktuna, M. & Kaçar, A. & Günaydın S. O. (2025). Gas Hydrates as a New Energy Resource. BRIQ Belt & Road Initiative Quarterly 6(3), 351-374.

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
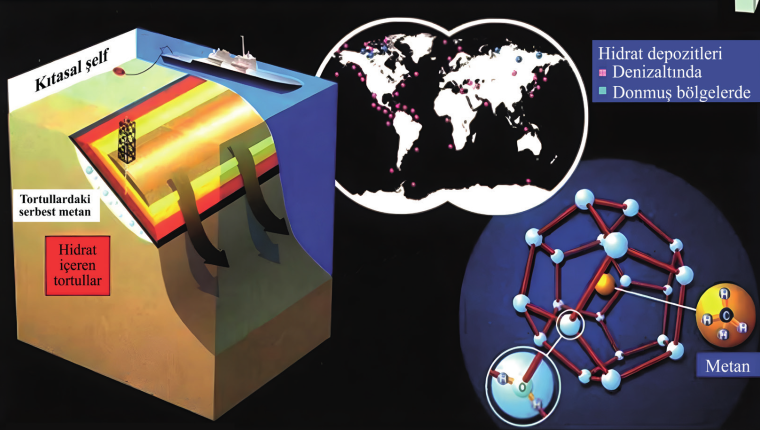
Gas hydrates, solid ice-like structures formed by water and methane molecules, are emerging asa critical future energy resource, offering abundant reserves of cleaner-burning methane. Thesereserves have the potential to enhance energy security, diversify energy portfolios, and supportthe transition from traditional hydrocarbons to more sustainable energy systems. Globally, nationssuch as Japan, China, the United States, India, South Korea, and Canada are leading research anddevelopment in gas hydrates, making substantial investments in advanced technologies and fieldtests. These efforts aim to overcome the significant technical and economic challenges currentlylimiting commercial-scale production. Türkiye’s proximity to significant gas hydrate deposits,particularly in the Black Sea, presents a notable strategic opportunity. It is imperative that Türkiyecapitalizes on this unique positioning by transforming these inherent advantages into long-termcompetitive strengths. The confirmed gas reserves in the Black Sea exemplifies such potential.
