Gürcan, E.C. (2020). International security after the Arab Spring: Domestic and ınternational sources of the Syrian and Libyan conflicts (2011-2020). Belt & Road Initiative Quarterly, 1(2), 65-80.

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
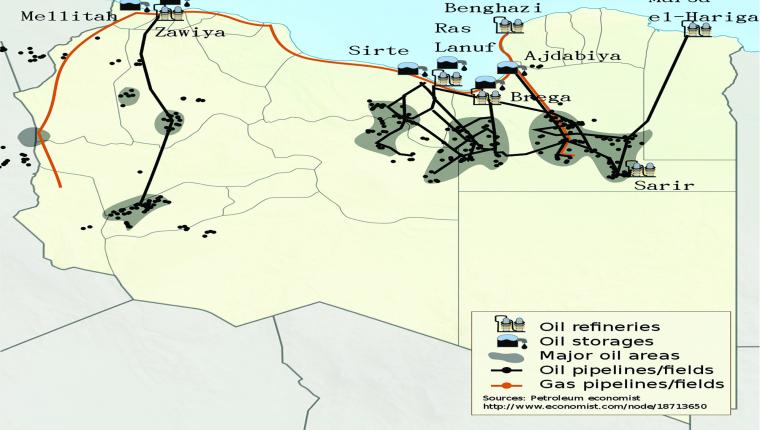
The so-called Arab “Spring” may be considered as the most significant geopolitical event and the largest social mobilization that have shaped Greater Middle Eastern politics in the post-Cold War era. The present article examines how this process turned into an Arab “Winter”, having led to the world’s largest humanitarian crises since World War II. Using a geopolitical-economy framework guided by narrative analysis and incorporated comparison, this article focuses on the countries where the Arab Spring process led to gravest consequences: Syria and Libya. The research aim is to develop a comprehensive and multi-dimensional framework that gives due attention to the dialectics of internal and external factors underlying armed conflicts. I argue that the failure of Syria’s Baathist development project constitutes an important root cause for Syria’s tragic destabilization, since it created a favorable environment for foreign intervention and the exploitation of ethno-religious differences by foreign powers. The same can be said of Libya’s domestic policy failures inscribed in its extractivism, liberalization and nepotism, which are coupled with its cultural and socio-demographic vulnerabilities. As far as the external factors of the Syrian conflict are concerned, the evidence suggests that the transformation of ethno-religious tensions into a proxy war is strongly mediated by the foreign policy imperatives of key countries involved in the Syrian conflict. In both cases, geopolitical factors – including energy and human security, military alliances, and foreign-policy commitments – seem to have served as strong incentives for the emergence and diffusion of conflicts.
Keywords: Arab Spring; human security; international development; international security; political ecology; political economy
